Improved effectiveness of dispersion processes with bead mills
The milling equipment being used in the manufacture of paints and inks is always purchased for the production of specific products. Frequently, with the passage of time, these products change formulations, raw materials (pigments), etc. The effectiveness of the grinding machines may vary after some change and it is at this moment when it is necessary to adapt the type of beads to be used. Let’s see what grinding elements we use in O+B mills and compare their performance with each other.
GRINDING ELEMENTS IN THE O+B MILLS
Comúnmente llamadas microesferas, sus características físicas determinan la efectividad de cualquier proceso de molienda.
Los tipos de microesferas utilizados habitualmente son los siguientes:
Commonly called microspheres, their physical characteristics determine the effectiveness of any grinding process.
The types of microspheres commonly used are as follows:
- Glass
- Zirconium silicate, also called Zirconium silicate
- Yttrium-stabilized zirconium oxide, commonly called Yttria
- Tungsten carbide, also called tungsten carbidez
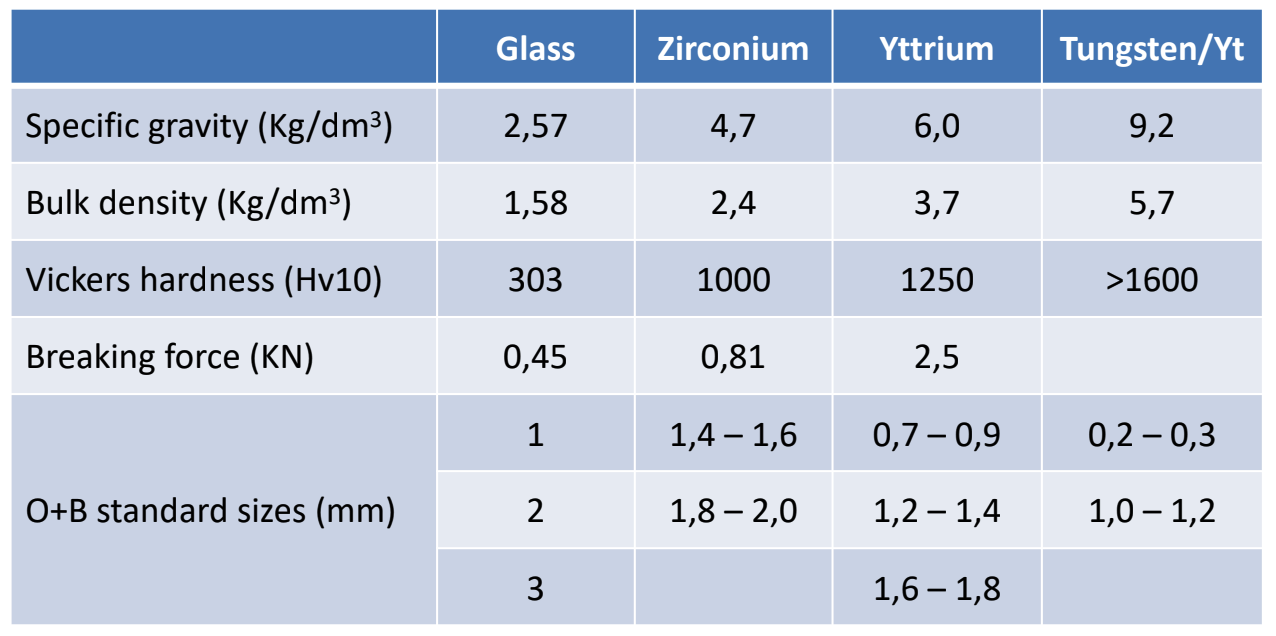
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE GRINDING ELEMENTS
Glass microspheres are almost entirely replaced by Zirconium or Ytrium.

Characteristics:
- Material density: 2.57 Kg/dm3, apparent 1.58 Kg/dm3.
- Vickers hardness: 303 HV 10
- Diameters in stock O+B: 1, 2 and 3 mm
Zirconium microspheres marketed by O+B have the following characteristics:
- Material density 4.7 Kg/dm3 (real), apparent 2.4 Kg/dm3.

- Vickers hardness (*1): 1000 HV 10
- DVickers hardness (*1): 1000 HV 10
Ytrium microspheres in O+B have the following characteristics:

- Material density: 6 Kg/dm3, apparent 3.7 Kg/dm3
- Vickers hardness: 1250 HV 1
- Available diameters O+B : 0.7 – 0.9 mm,
1,2 – 1,4 mm and 1,6 – 1,8 mm
Tungsten microspheres are recently used in O+B and are in the testing phase. The characteristics are:
- Material density: 9.2 Kg/dm3, apparent 5.7 Kg/dm3.
- Vickers hardness: >1600 HV 0,5
- Current test diameters: 1.0 – 1.2 mm
SUMMARY CHARACTERISTICS OF THE GRINDING ELEMENTS
COMPARISON OF THE DIFFERENT GRINDING ELEMENTS
1. In order to establish the comparison, two water-based bases were chosen for the manufacture of ink applicable to plastic substrates:
- Black base: with a pigment content of 40% Carbon Black (inorganic).
- Yellow base: with a pigment content of 41% of benzyl yellow (organic).
2. The mill used for this test was our 1/4” Pilotmill.
The configuration used in all cases has been:
- 275 micron sieve
- Turbo impeller
- Cooling temperature selected at 5ºC
- Product quantity of approximately 10 liters
- Speeds maintained between 90-100% of maximum speed (1595rpm)
3. Comparison methodology:
- Grinding was carried out for 3 hours, taking samples every 20 minutes.
- The particle size was analyzed in a laser measuring equipment type Microtrac S3500.
- The results obtained were plotted in graphs to visualize the differences between the different sizes and materials of the microspheres.
- The values have been expressed differentiating the two types of pigments.
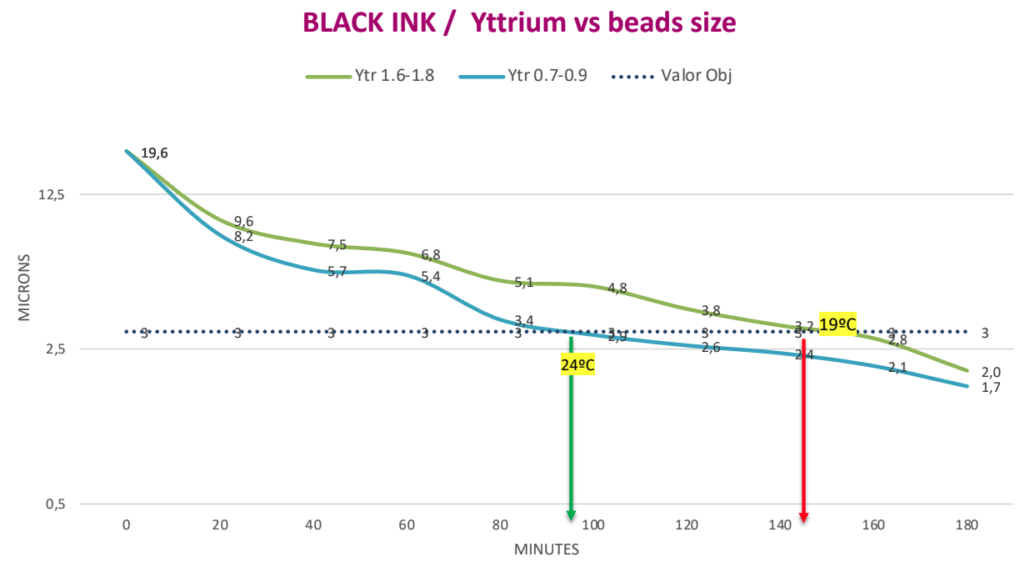
Targeted fineness 3 ?. Milling time with Yttrium beads 1,6 – 1,8 mm is 145 minutes. Milling time with Yttrium beads of 0,7 – 0,9 mm is 90 minutes. Time saving is 50 minutes or 34% of the milling time.
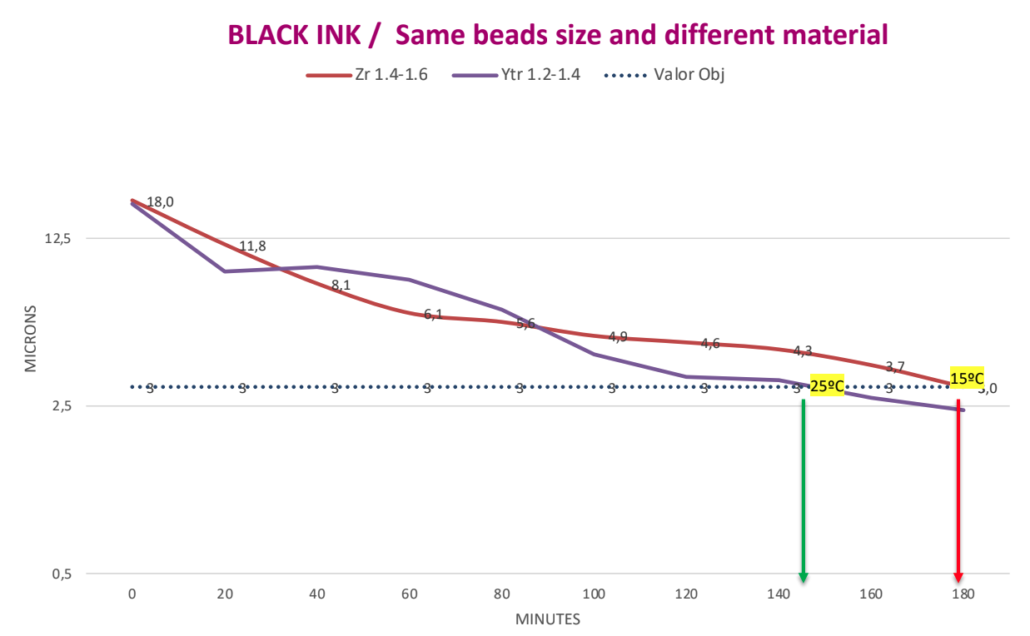
Targeted fineness 3 ?. Milling time with Yttrium beads 1.2 – 1.4 mm is 145 minutes. Milling time with Zirconium beads of 1.4 – 1.6 mm is 180 minutes. Time saving is 35 minutes or 19% of the milling time.

Targeted fineness 3 ?. Milling time with Tungsten beads 1.0 – 1.2 mm is 70 minutes. Milling time with Yttrium beads of 0.7 – 0.9 mm is 90 minutes. The time saving is 20 minutes or 26% of the milling time.Nano scale particles of 0.6 ? are reached within 165 minutes with Tungsten beads. It cannot be acjieved with Yttrium beads.
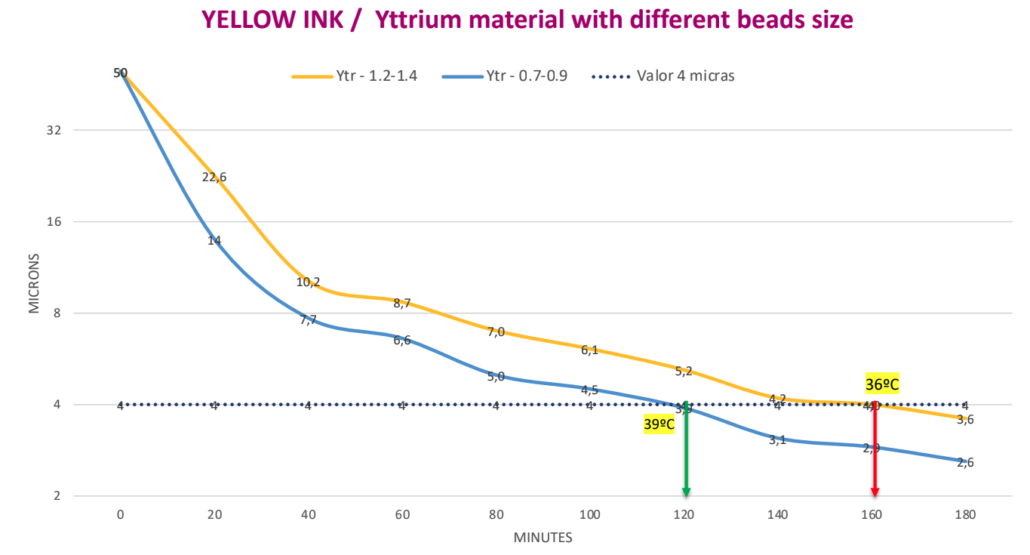
Targeted fineness 4 ?. Milling time with Yttrium beads 0.7 – 0.9 mm is 120 minutes. Milling time with Yttrium beads of 1.2 – 1.4 mm is 160 minutes. Time saving is 40 minutes or 25% of the milling time.
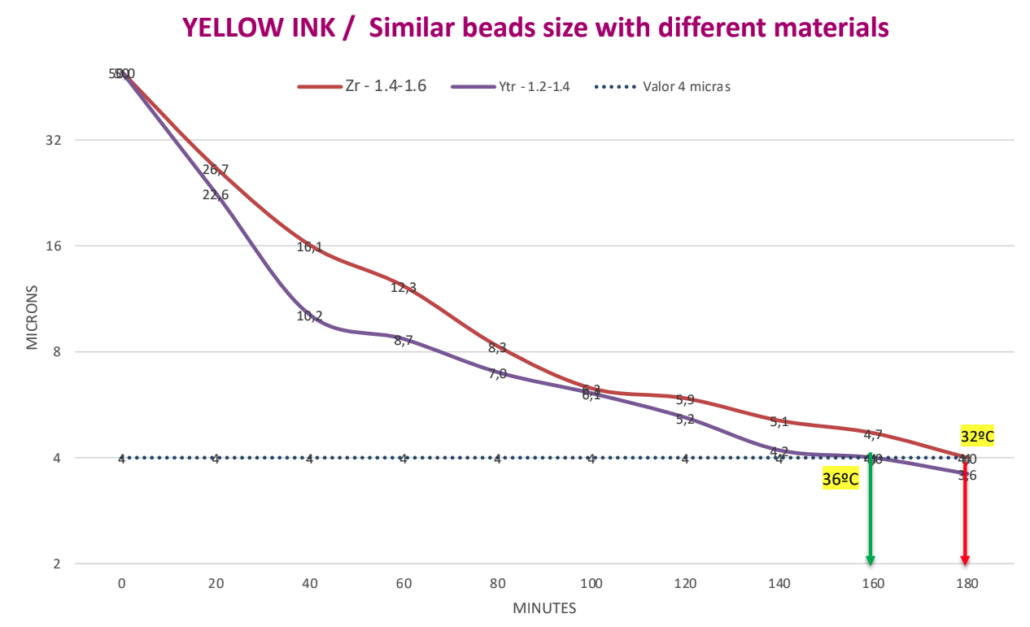
Targeted fineness 4 ?. Milling time with Zirconium beads 1.4 – 1.6 mm is 180 minutes. Milling time with Yttrium beads of 1.2 – 1.4 mm is 160 minutes. Time saving is 20 minutes or 11% of the milling time.
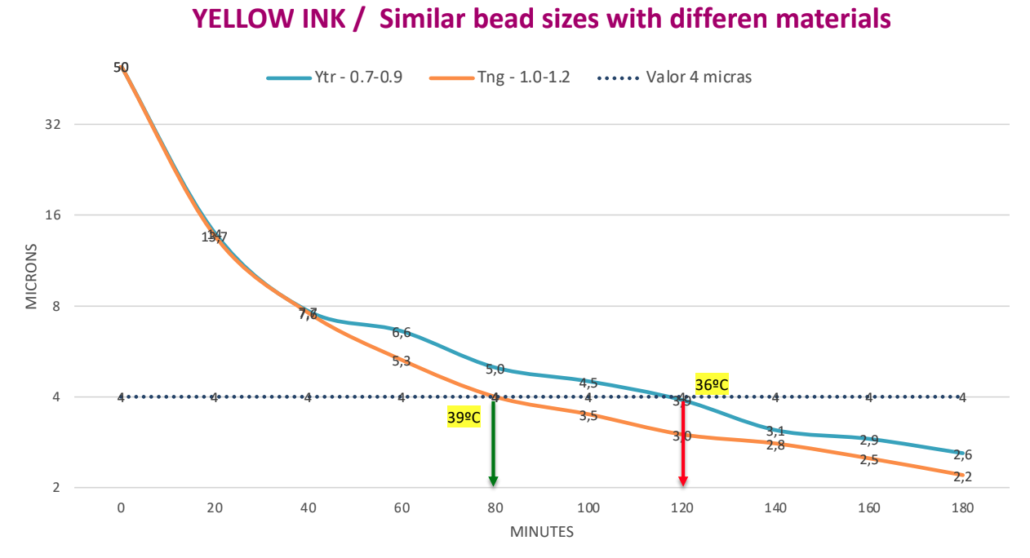
Targeted fineness 4 ?. Milling time with Tungsten beads 1.0 – 1.2 mm is 80 minutes. Milling time with Yttrium beads of 0.7 – 0.9 mm is 120 minutes. Time saving is 40 minutes or 33% of the milling time.
CONCLUSIONS BLACK & YELLOW: Zirconium, Yttrium or Tungsten
By using higher density Yttrium or Tungsten microspheres, greater effectiveness is achieved and we can see this by comparing the significant time savings.
The cost of Yttrium or Tungsten microspheres is higher than Zirconium microspheres.
- In the case of carbon black to reach a size of 3 microns we have to:
- Zirconium 1.4-1.6 takes 180 minutes.
- Yttrium 1.2-1.4 takes 19% less.
- Yttrium 0.7-0.9 takes 47% less.
- Tungsten 1.0-1.2 takes 61% less.
- In the case of yellow to reach a size of 4 microns we have to:
- Zirconium 1.4-1.6 we take 180 minutes.
- Ytrium 1.2-1.4 takes 11% less.
- Yttrium 0.7-0.9 takes 33% less.
- Tungsten 1.0-1.2 takes 56% less.
FINAL CONCLUSIONS
- At a general level, we can say that obtaining the particle size will always depend on the nature of the pigment. And particle size reduction targets down to 3 or 4 microns can be obtained with any type of microspheres.
- With the products tested, we can say that, at similar bead size, 3 or 4 micron sizes are best obtained with higher density beads such as Tungsten beads. This type of beads heat the products more and require more power from the equipment. Temperature increases can range from 5 to 10 oC depending on the product being processed and the recommended power increase would be 10%.
- Ytrium beads of 0.7 – 0.9 mm offer good results. The current prices of these grinding elements allow a good balance of price and performance to be found. Many users have opted for the frequent use of this type of beads.